Lab 02
PSYC480
Dr Usman Afzali
University of Canterbury
3/1/23
Recap
Pipeline
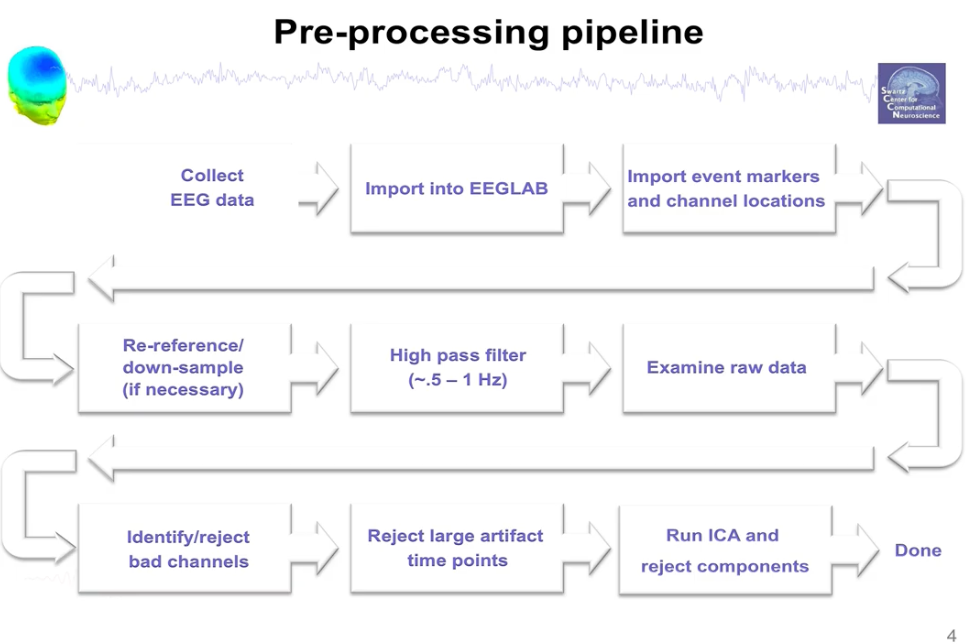
Referencing and Filtering
Referencing
- Why do we reference?
- Procedure: Use the available dataset from Learn
Lab 2 demo dataset. Task 1: Read the dataset into EEGLab, and report attributes. Insert a screenshot of the attributes too.Task 2: Elaborate on what the attributes say about referencing? And how we remedy that?
Referencing to M2
- Use
Tools -> re-reference the data. Task 3: Compare the attributes to the original dataset. Is there any discrepancy? If yes, why?- If you haven’t picked answer to “why” yet, plot the data again and observe closely.
Filtering
- Why do we filter data?
- Many sources of noise, such as the 60Hz line noise, consist mainly of very high frequencies or very low frequencies, whereas most of the useful information in an EEG or ERP waveform is at intermediate frequencies (between approximately 0.1Hz and 50Hz). (Cacioppo, Tassinary, and Berntson 2016)
Filtering contd….
Consequently, the noise can often be reduced with minimal impact on the EEG/ERP waveform by filtering out the very low and/or very high frequencies.
Delorme recommends filtering at 0.5.
Use
Tools -> Filter data -> basic FIR Filter. Type 0.5 in theLower edgeDC offset: https://relaytraining.com/what-is-dc-offset-ask-chris/
Visaul inspection….
Task 4: FromEdit, selectchannel locations- Plot channels as
2-D - Do you see any anomaly? Comment!
- Submit this as a pdf on Learn.
The END
References
Cacioppo, John T., Louis G. Tassinary, and Gary G. Berntson, eds. 2016. Handbook of Psychophysiology. Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/9781107415782.