Introduction to Neuroscience - 2 + Methods in Neuroscience
PSYC480
Dr Usman Afzali
University of Canterbury
2/28/24
Kauhau
- Fundamentals of Neuroscience
- Methods in Neuroscience
Note Taking (from SAS) …
Change of the Lecture Venue
Change of lecture venue. From next Wednesday onwards, we will be moving to Psyc Soci 210 (capacity = 27 seats).
Fundamentals of Neuroscience
What is Neuroscience?
- Perception, thinking, understanding, control of movement
- Experimental psychology + physiology
- Research: perception, control of movement, sleep and walking, reproductive/ingestive/emotional behaviour, learning, memory
- Examples of neuroscience subfields
- Computational neuroscience
- Tools to conduct neuroscientific research
History
- 7th Century: Descartes and control of behaviour
- 19th Century: Muller and removing organs for study
- Contemporary neuroscience
Ethical Issues
- Animal research
- Human research
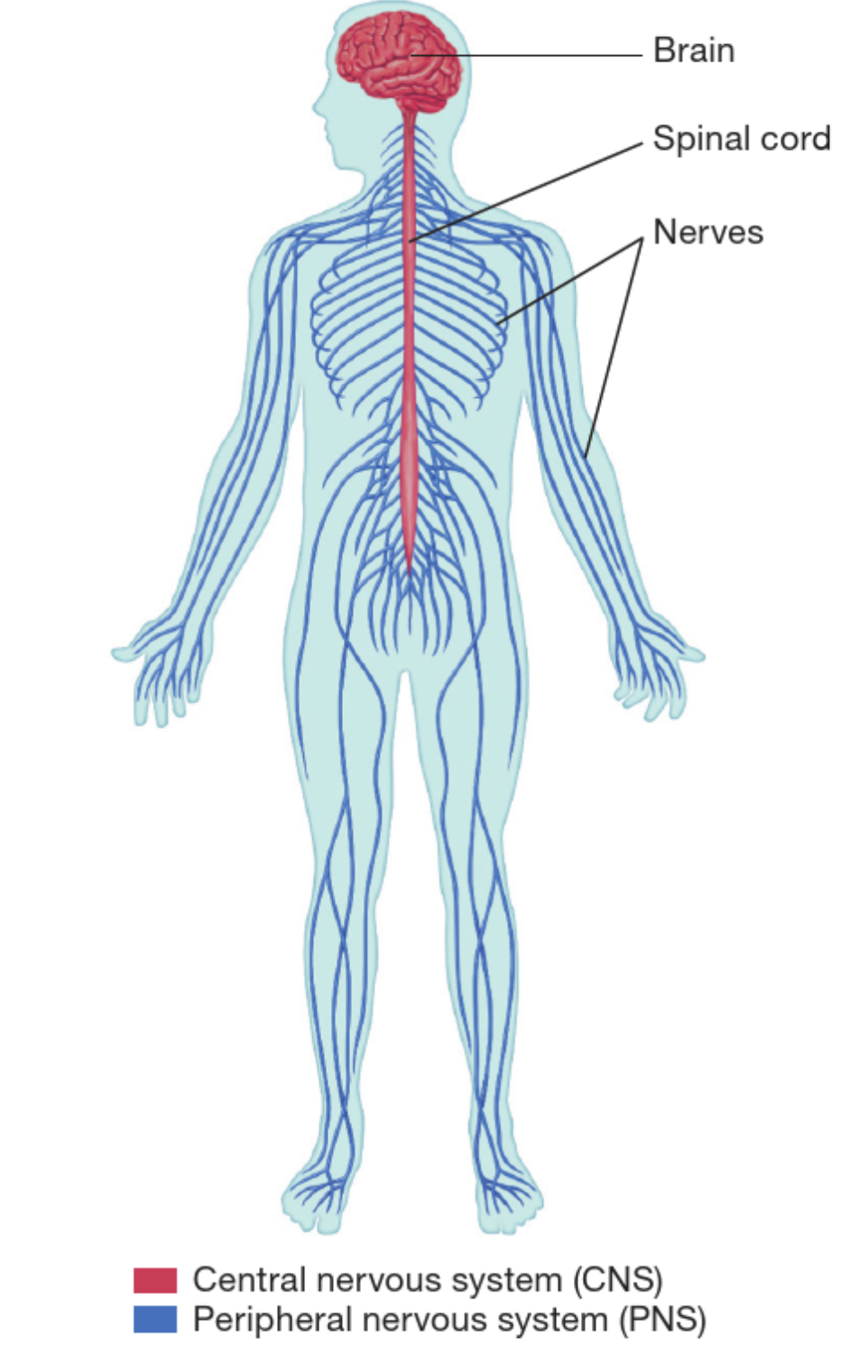
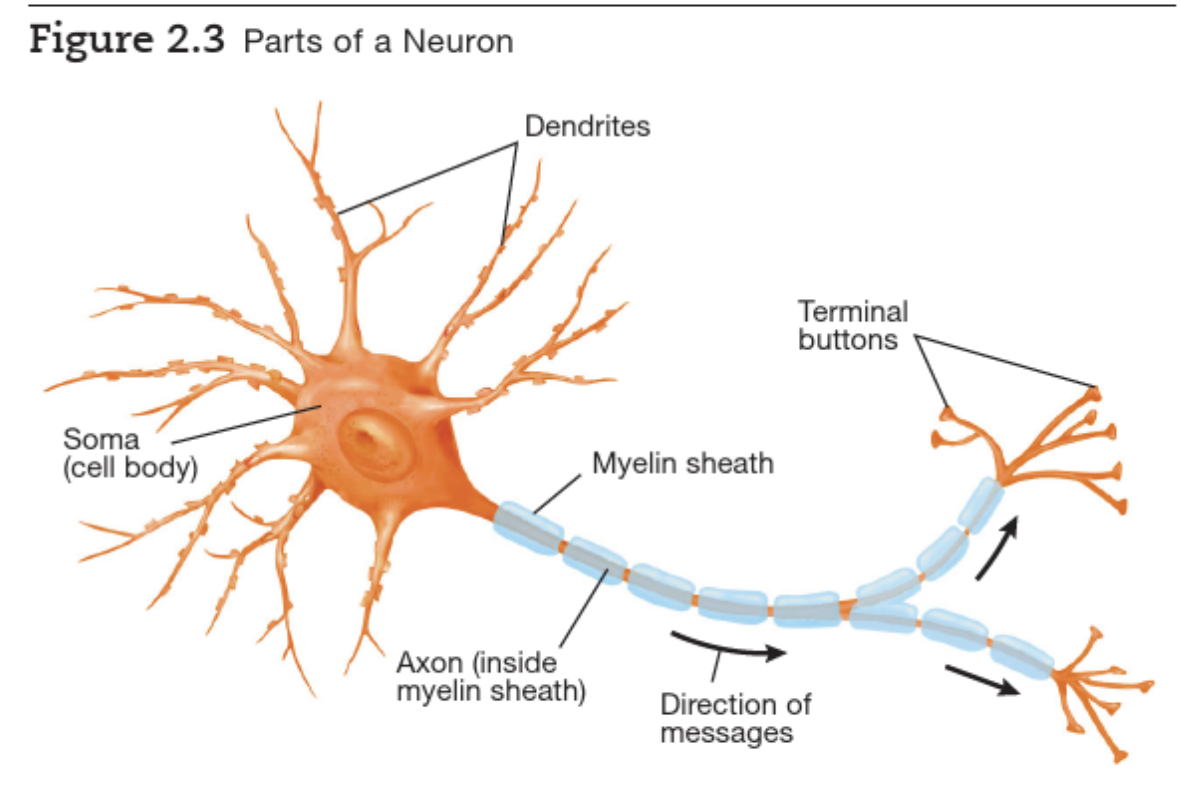
Neuron
Structure
- Axon
- Dendrite
- Cell body
Neuron, CNS and PNS
Physiology of Neuron
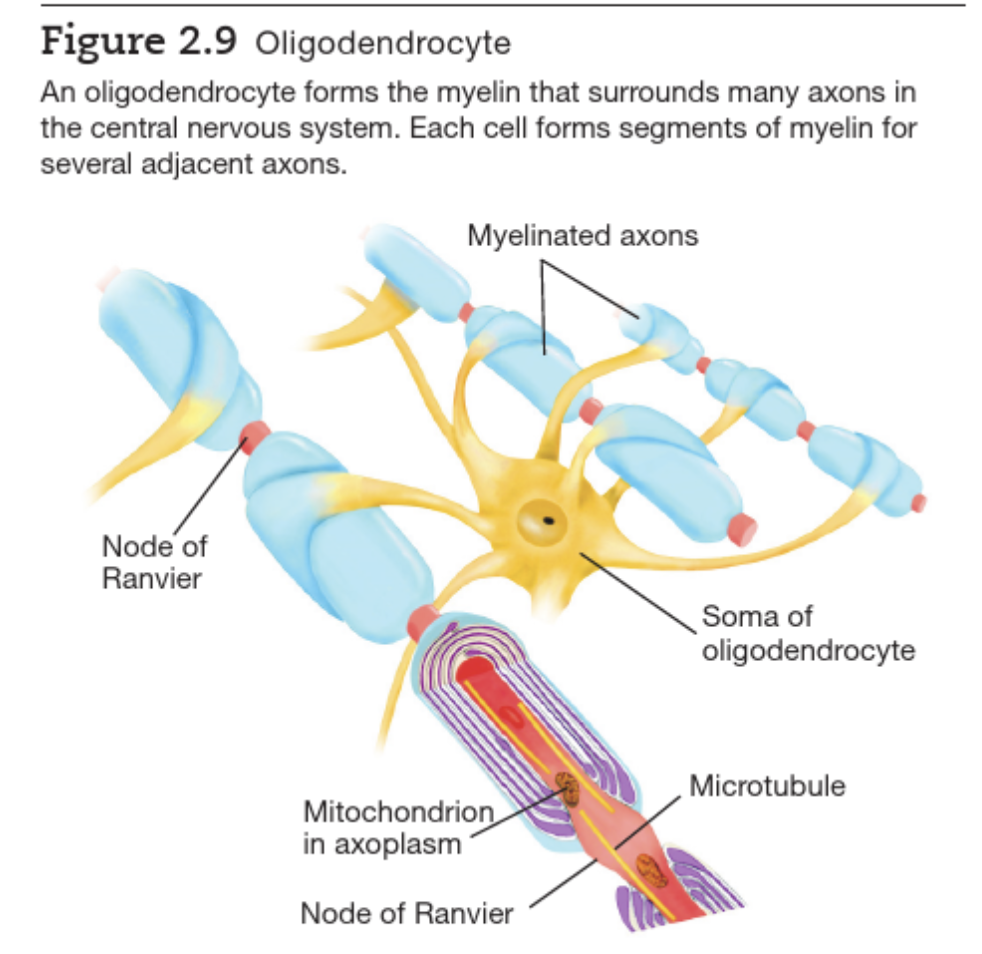
Supporting cells of Neuron
- Glia: nerve glue
- Astrocyte: physical support and clean debris
- Oligodendrocyte: support axons and produce myelin sheath
- Schwann cells: PNS
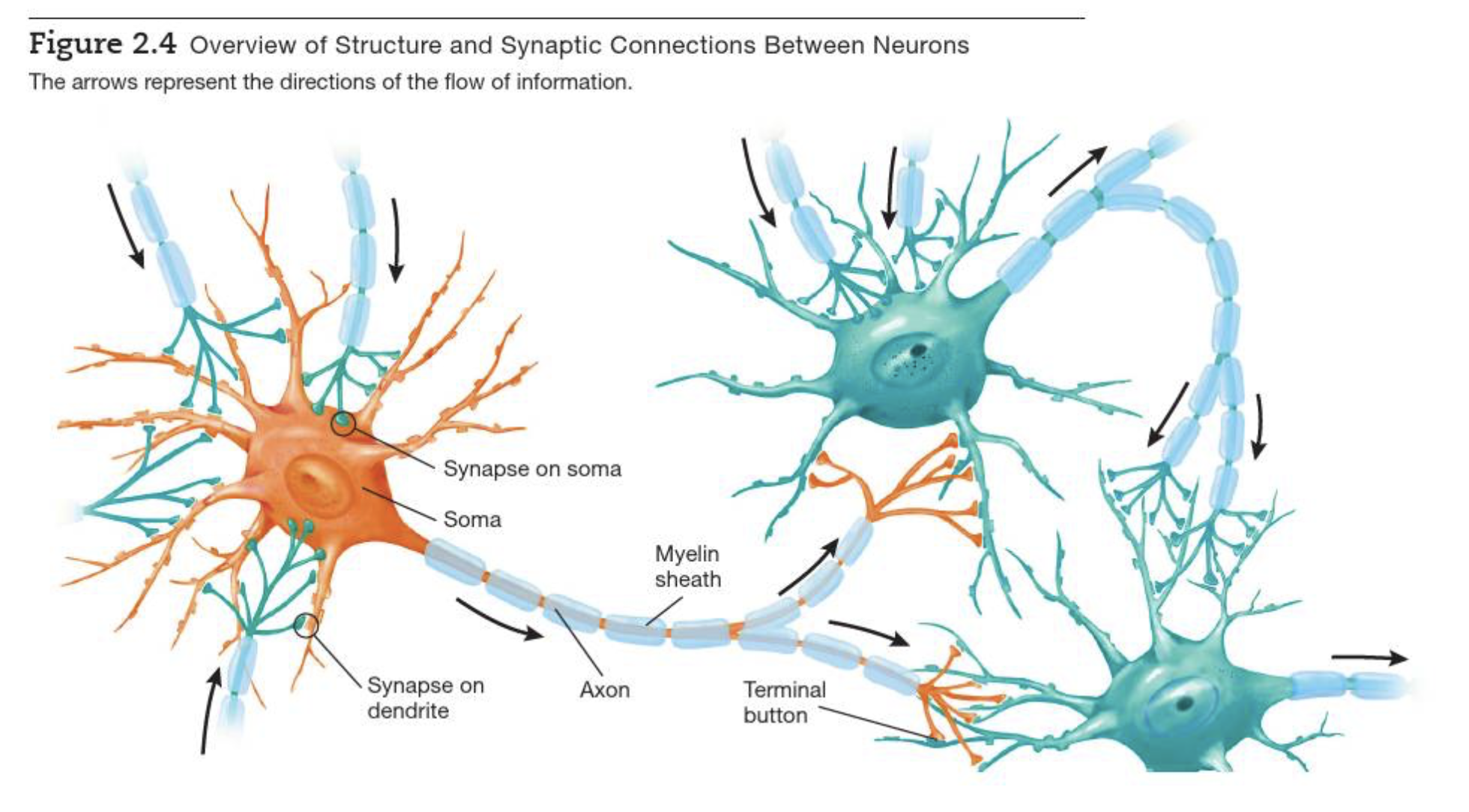
Neuron communication 1
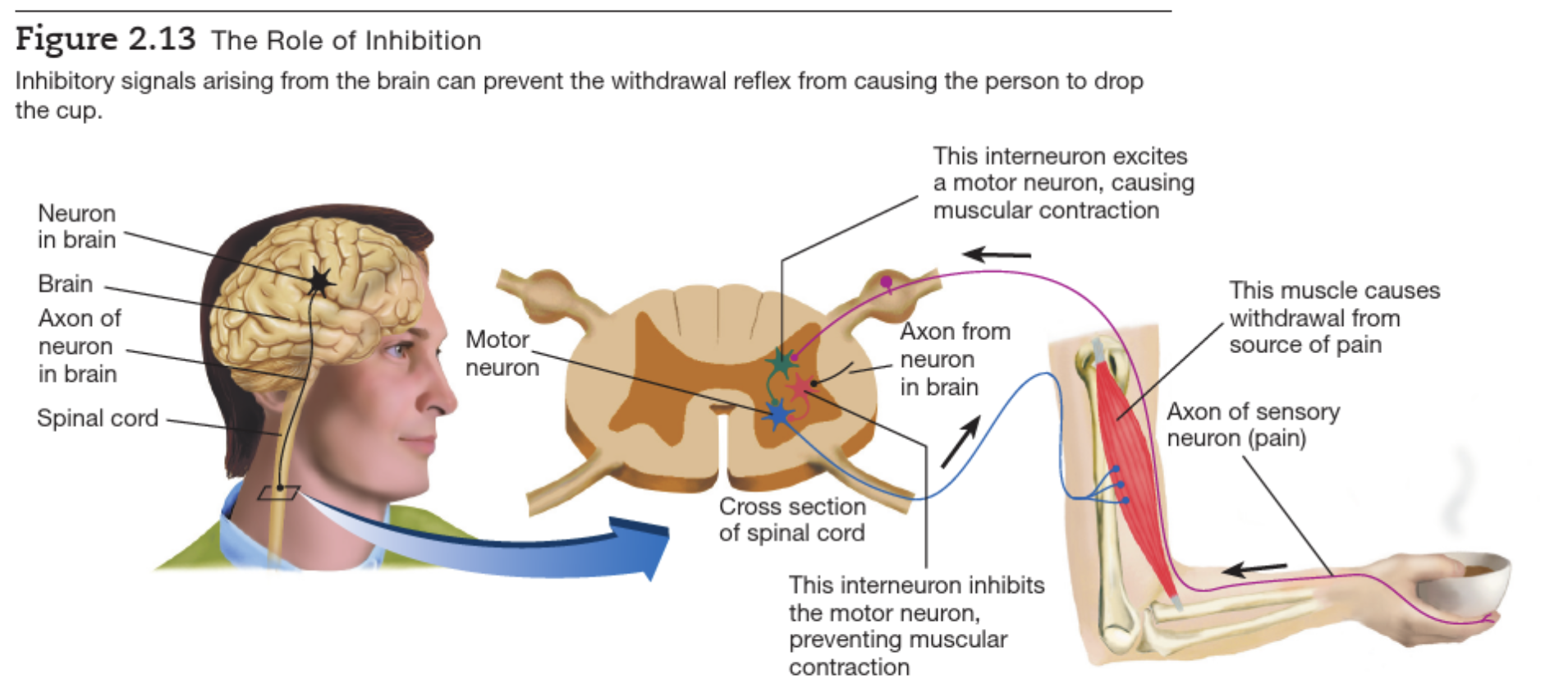
Withdrawal reflex
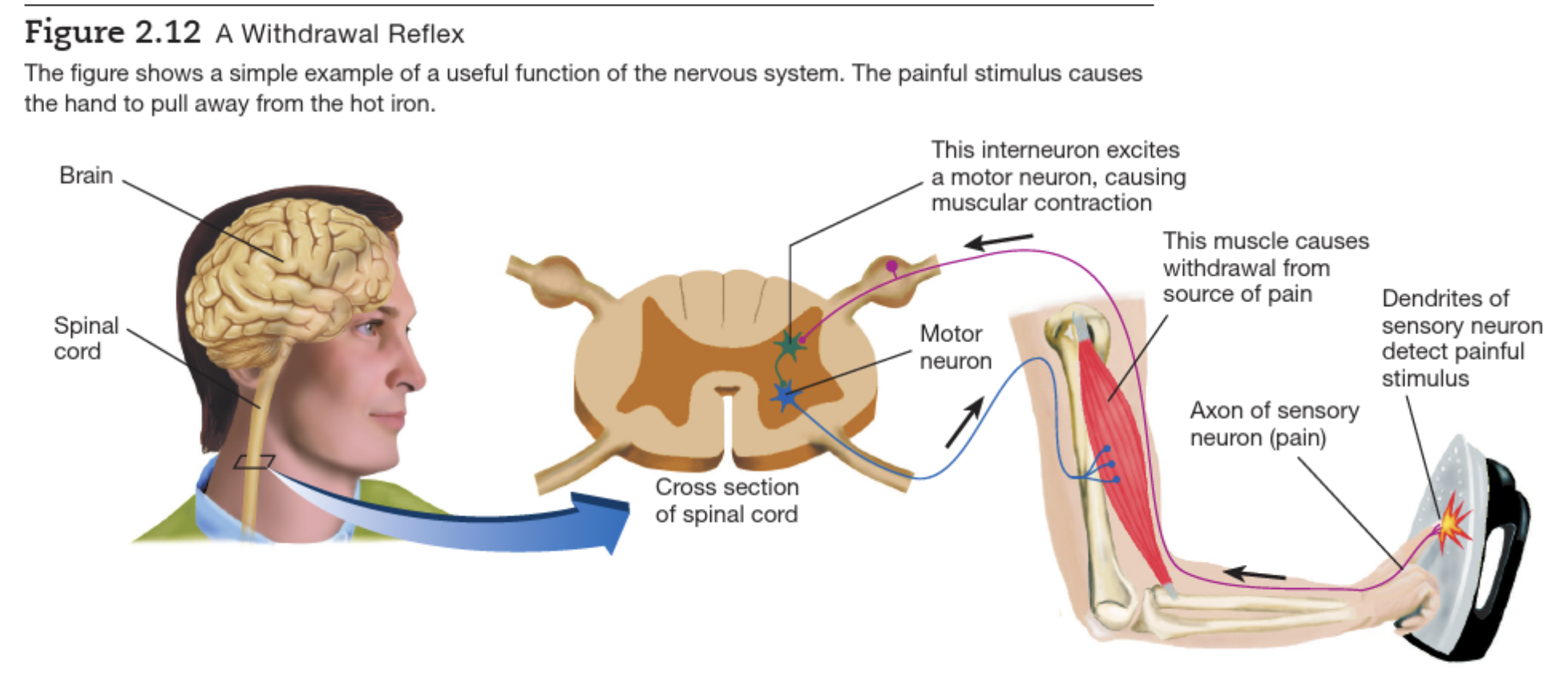
Neuron communication 2
Inhibition
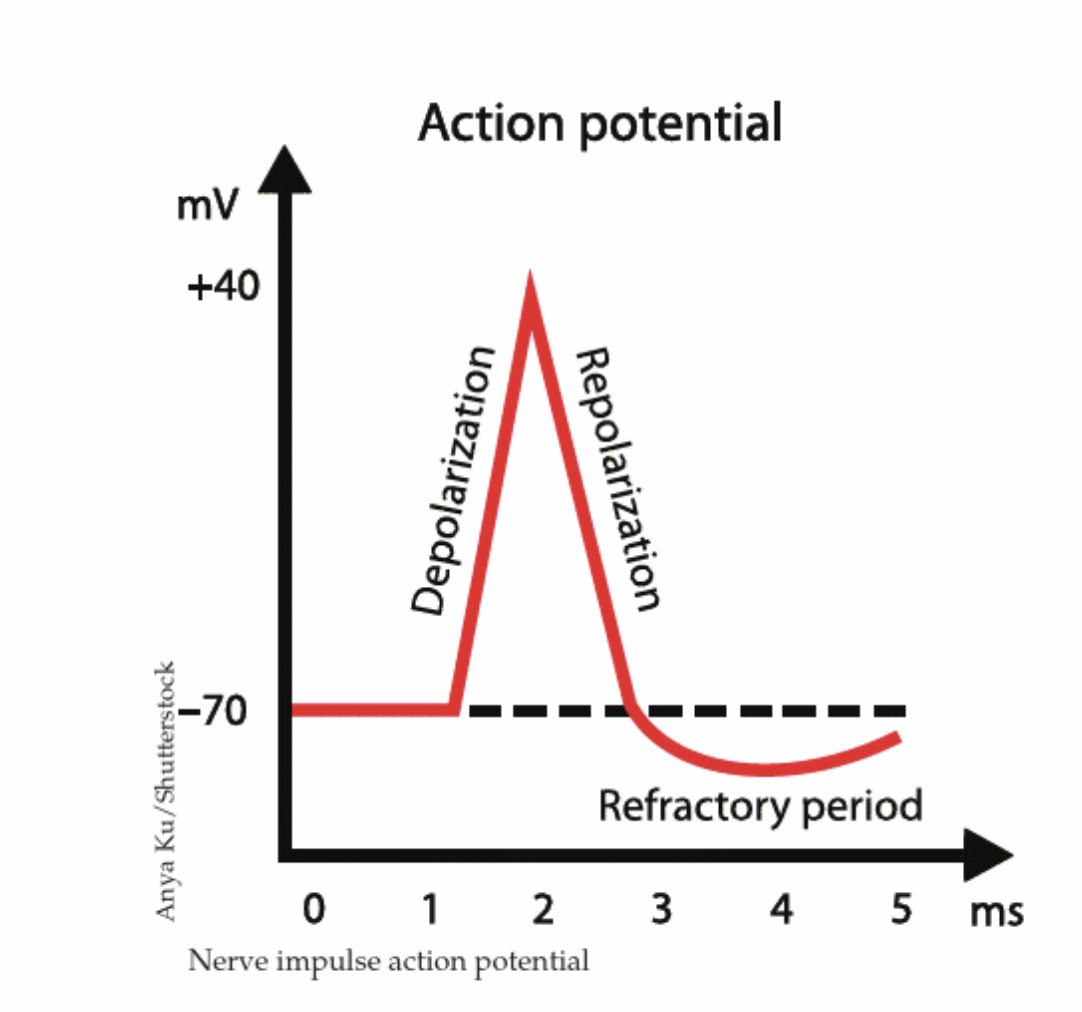
Action Potential
Electrical event in the neuron
- Negative charge of -70mV inside the axon membrane - resting potential
- Any difference: membrane potential
- hyperpolarisation vs. depolarisation
Synapse
- The role of neurotransmitters
- Presynaptic membrane, synaptic cleft, postsynaptic membrane
- Postsynaptic potentials: EPSP and IPSP
- Termination of postsynaptic potentials
Synapse types
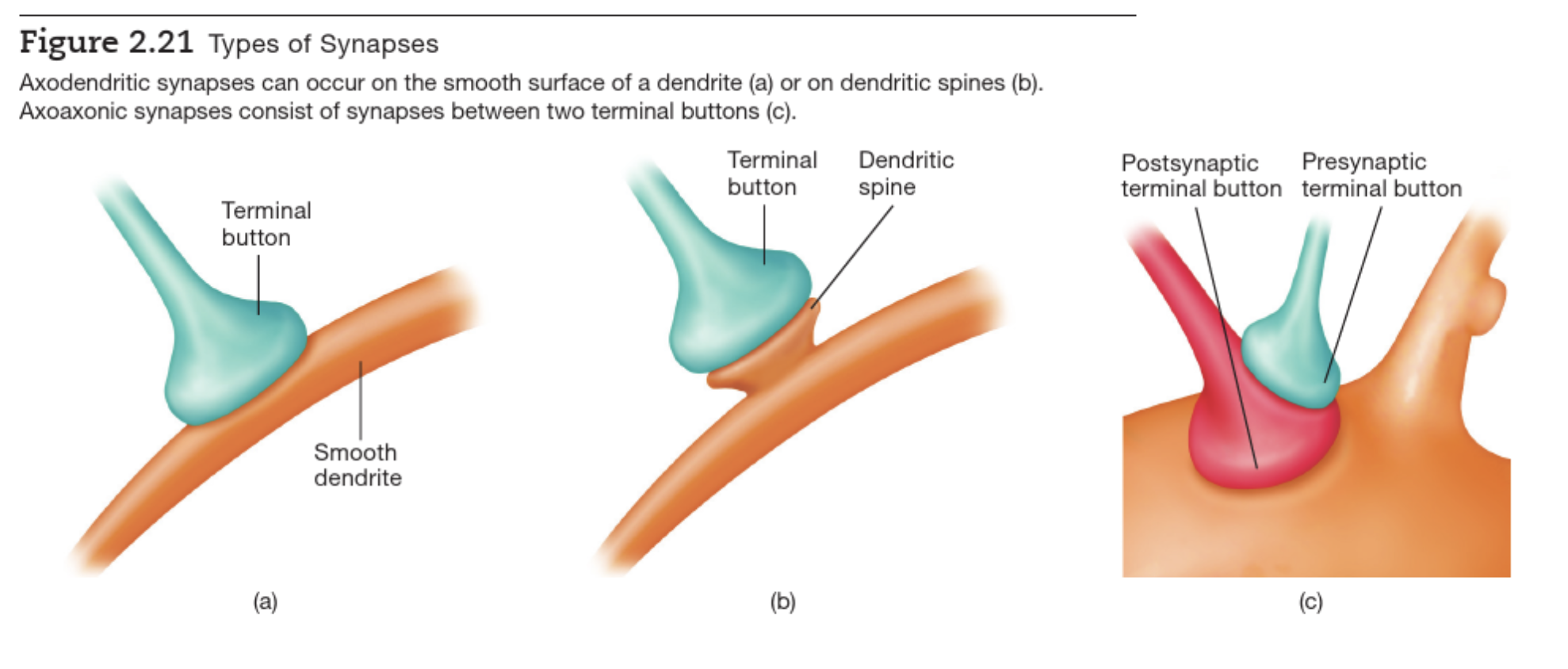
CNS Structure
Brain Development
Pre- and post-natal
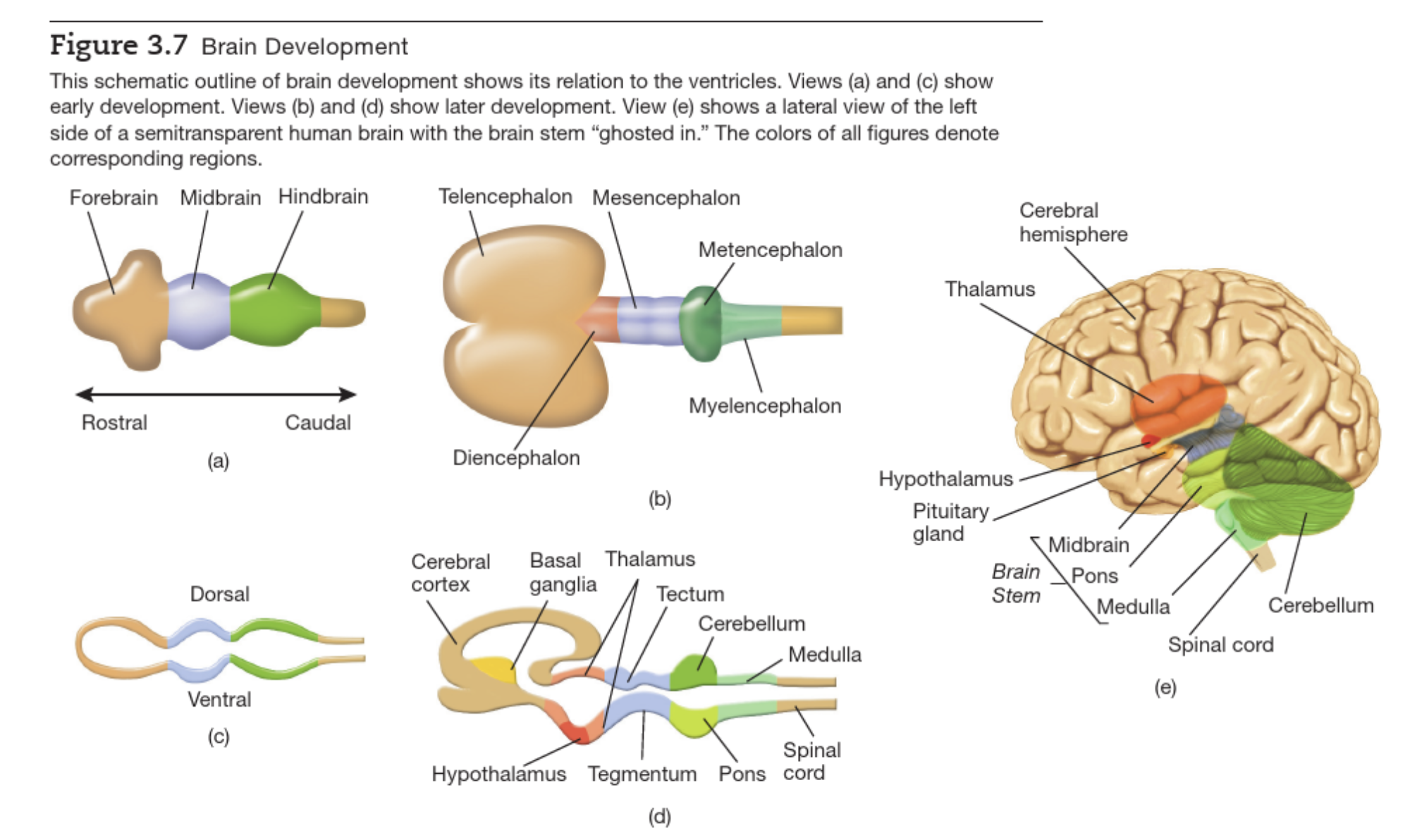
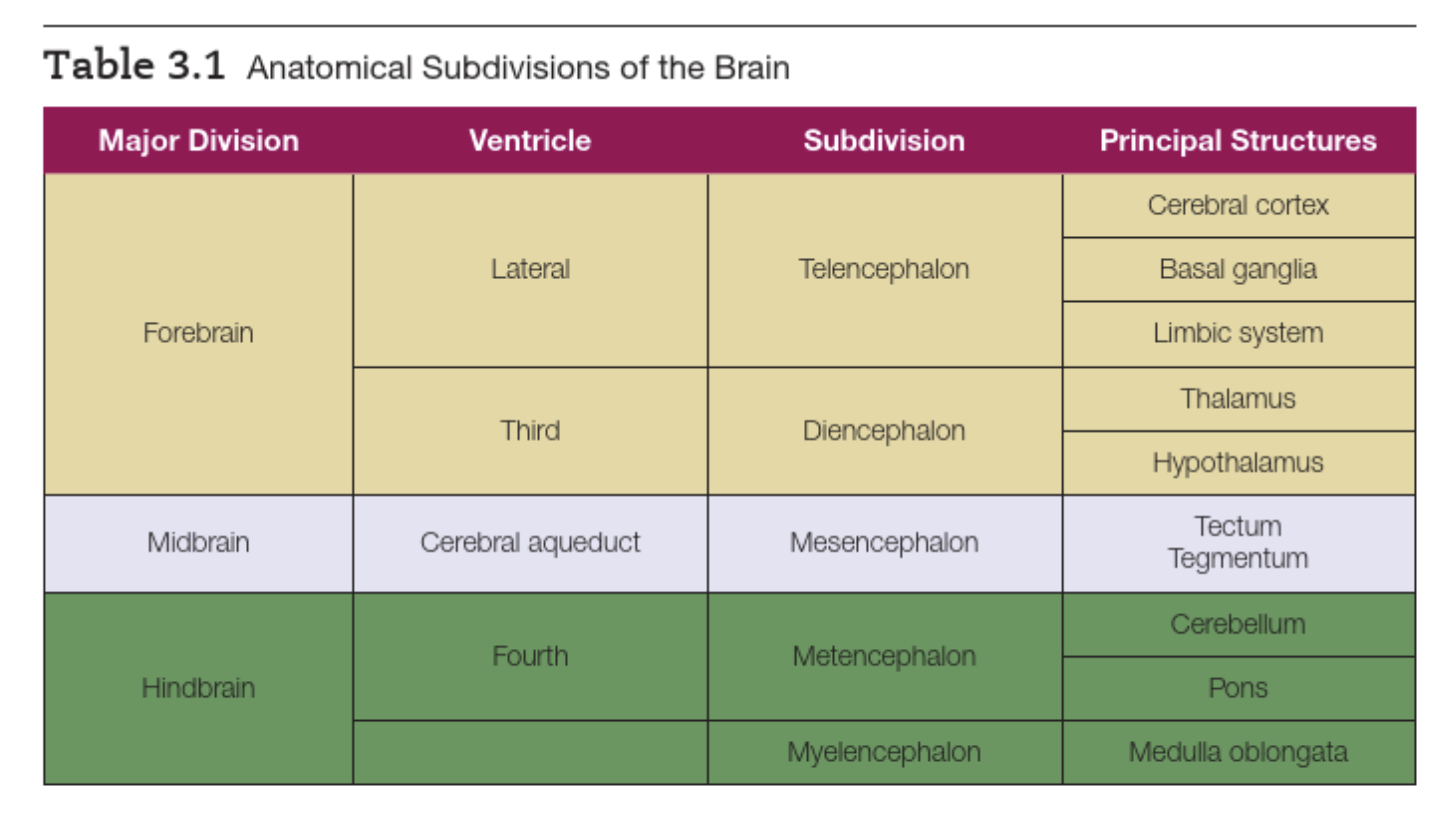
Sub-divisions
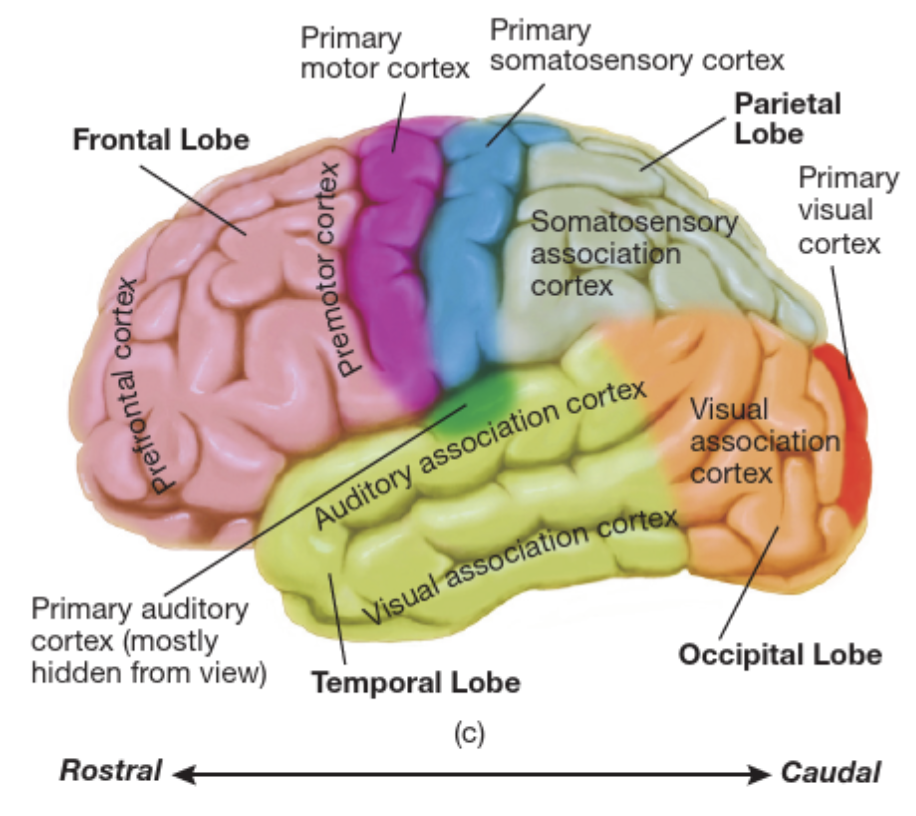
Cerebral Cortex
- Surrounds the cerebral hemispheres
- Greatly convoluted; consisting of sulci (small grooves), fissures (large grooves), and gyri (bulges between adjacent sulci or fissures)
- Greatly enlarged surface area of the cortex, compared with a smooth brain
Four Lobes

Four Lobes…
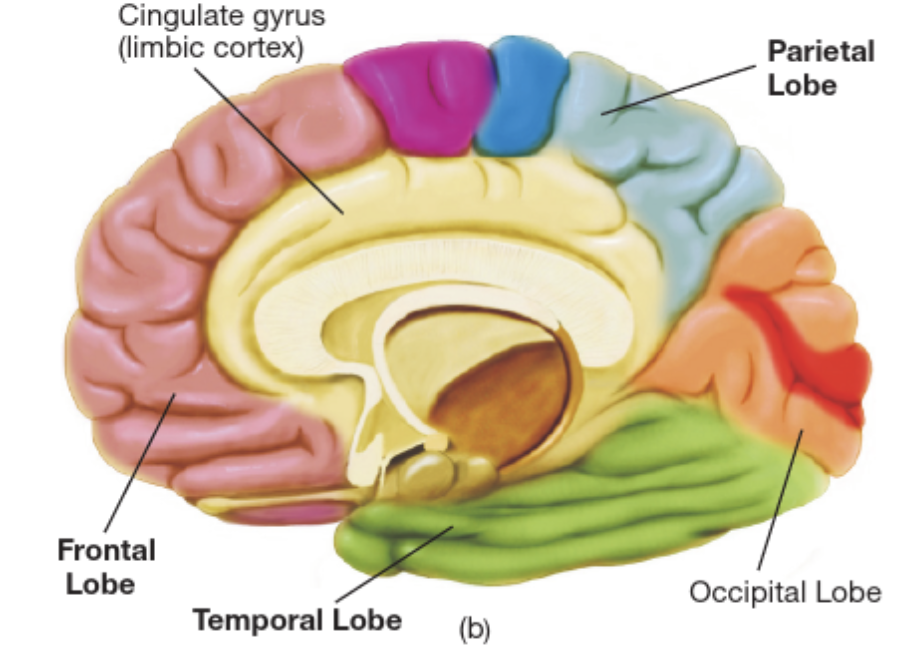
Four Lobes…
BREAK TIME
Methods in Neuroscience
Functional Neuroimagining
- Introduction and function
- Uses
- Limitations (functional, spatial, and temporal)
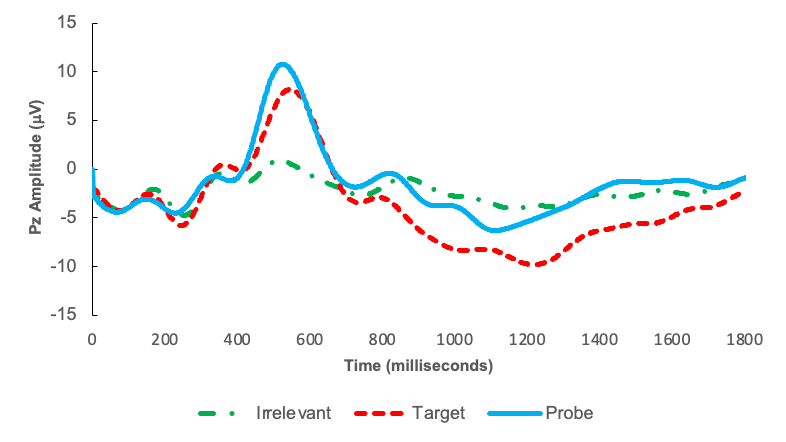
EEG/ERP
- Introduction and function
- Uses
- Limitations
(Cacioppo, Tassinary, and Berntson 2016)
High Performance microsegmentation
- Introduction and Use
- Examples
Microstates

THE END
References
Afzali, M. Usman, Alex P. Seren-Grace, Robin W. Palmer, Ewald Neumann, Sarah Makarious, Debra Wilson, and Richard D. Jones. 2022. “Detection of Concealed Knowledge via the ERP -Based Technique Brain Fingerprinting : Real-Life and Real-Crime Incidents.” Psychophysiology 59 (11). https://doi.org/10.1111/psyp.14110.
Cacioppo, John T., Louis G. Tassinary, and Gary G. Berntson, eds. 2016. Handbook of Psychophysiology. Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/9781107415782.
Carlson, Neil R., and Melissa A. Birkett. 2017. Physiology of Behavior. Twelfth;Global; Book, Whole. Harlow, Essex: Pearson. https://go.exlibris.link/wyZtfK4C.