Lab 03
PSYC480
University of Canterbury
2024-04-23
EEG Microstates
- Definition
- Use
- Re-processing
Microstates Definition
“EEG microstates are brief, recurring periods of stable brain activity that reflect the activation of large-scale neural networks. The temporal characteristics of these microstates, including their average duration, number of occurrences, and percentage contribution have been shown to serve as biomarkers of mental and neurological disorders” (Kleinert, Nash, et al. 2024).
Two major types
- Resting EEG Microstates
- ERP Microstates
The use of Microstates
“Recent publications demonstrate the potential of microstate research to contribute to a more sophisticated diagnosis, monitoring, prognosis, and prevention of mental disorders in clinical psychology and psychiatry. Microstate characteristics may serve as biomarkers of schizophrenia (da Cruz et al. 2020; de Bock et al. 2020), affective disorders (Al Zoubi et al. 2019; Damborská et al. 2019b; Murphy et al. 2020), anxiety disorders (Al Zoubi et al. 2019), ADHD (Férat et al. 2022a), and autism (D’Croz-Baron et al. 2019; Bochet et al. 2021). as mentioned in (Kleinert, Koenig, et al. 2024)”
Processing for Microstates analysis
EEG data processing (as described in the previous labs) has historically been recommended by many experts. However, recent research shows that the EEG data processing (or over-processing) could be counterproductive. Therefore, it is sensible to process the data to only the extent that is needed to obtain microstates that resemble the prototypical four to seven network types.
Processing continued….
To the best of my knowledge, it is important to use only the following processing steps:
- Add channel locations
- Filter 2-20 Hz
- Remove artefacts with ASR, but make sure to un-check the option
Remove channel if it is flat for more than (seconds), see Figure 1. - Reference to average and interpolate removed channels.
Processing continued….

Figure 1: Automatic artefact removal
Processing continued….
- From
Tools -> Microstates -> Obtain Microstate Maps, usek-meansmethod with a min of 4 and max of 5 maps, and setrestartsto 20, see Figure 2. - From
Plots ->… - Examine whether or not your obtained microstates resemble the prototypical four (or seven) network types (see Figure 3) (Nash et al. 2022).
Microstates menu

Figure 2
Typical MS Maps
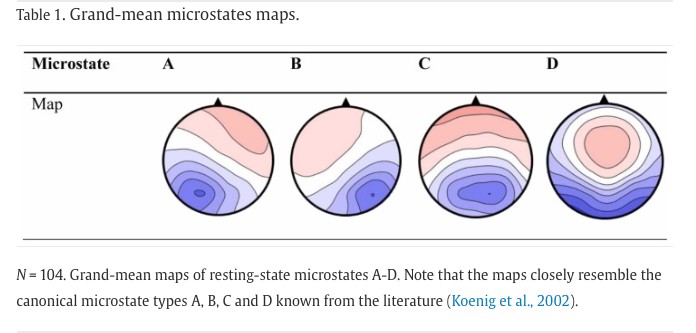
Figure 3: Four prototypical microstates (Nash et al. 2022)
Obtaining microstates
- Use
Lab 3 demodataset on Learn. - Conduct the necessary processing.
To submit
- Use the the
Lab 3 exercisedataset on Learn. - Conduct necessary processing.
- Identify microstate maps