Abstract
The Christchurch mosque attacks in 2019, committed by a radical right-wing extremist, resulted in the tragic loss of 51 lives. Following these events, there was a noticable rise in societal acceptance of Muslim minorities. Comparable transient reactions have been observed elsewhere. However, the critical questions remain: can these effects endure? Are enduring effects evident across the political spectrum? It is challenging to answer such questions because identifying long-term causal effects requires estimating unobserved attitudinal trajectories without the attacks. Here, we use six preattack waves of Muslim acceptance responses from the New Zealand Attitudes and Values Study (NZAVS) to infer missing counterfactual trajectories (NZAVS cohort 2012, N = 4,865; replicated in 2013 cohort, N = 7,894). We find (1) the attacks initially boosted Muslim acceptance; (2) the magnitude of the initial Muslim acceptance boost was similar across the political spectrum; (3) no changes were observed in negative control groups; and (4) two- and three-year effects varied by baseline political orientation: liberal acceptance was stable, conservative acceptance grew relative to the counterfactual trend. Overall, the attacks added five years of growth in Muslim acceptance, with no regression to preattack levels over time. Continued growth among conservatives highlights the attack’s failure to divide society. These results demonstrate the utility of combining methods for causal inference with national-scale panel data to answer psychological questions of basic human concern.
Important figure
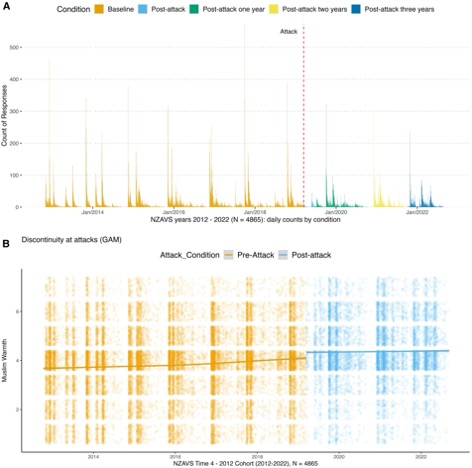
Figure 1: A) Histogram of rolling responses from the NZAVS. Responses in sequential order by periods of interest: (i) the preattack baseline (before 15 March 2019); (ii) the postattack interval in NZAVS Time 10 (2019 March 16 and the following three months); (iii) the + one-year post-attack period; (iv) the + two-years post-attack period; and (iii) the + three-years-post-attack period. B) Regression discontinuity analysis reveals a sharp increase in average acceptance of Muslims immediately after the attack, with no evidence for regression in the observed sample to the preattack acceptance average.
BibTeX citation
@article{bulbulia2023long,
title={Long-term causal effects of far-right terrorism in New Zealand},
author={Bulbulia, Joseph A and Afzali, M Usman and Yogeeswaran, Kumar and Sibley, Chris G},
journal={PNAS nexus},
volume={2},
number={8},
pages={1--16},
year={2023},
publisher={Oxford University Press US}
}